Alzheimer’s Research UK Conference 2019
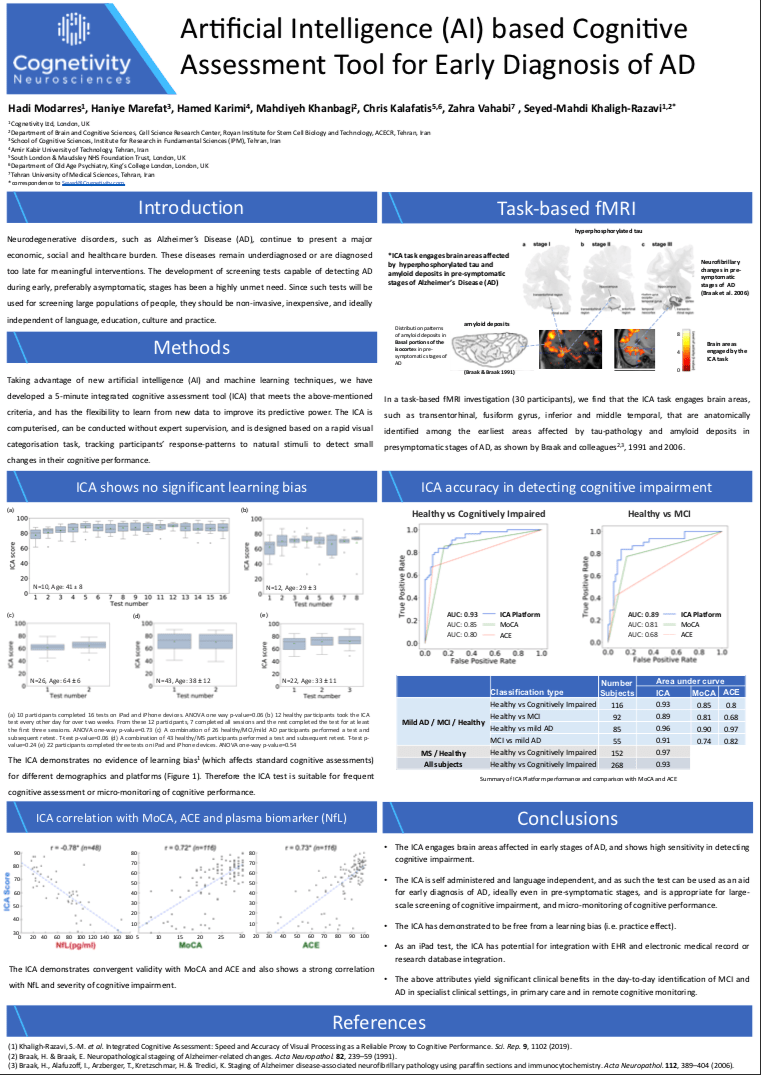
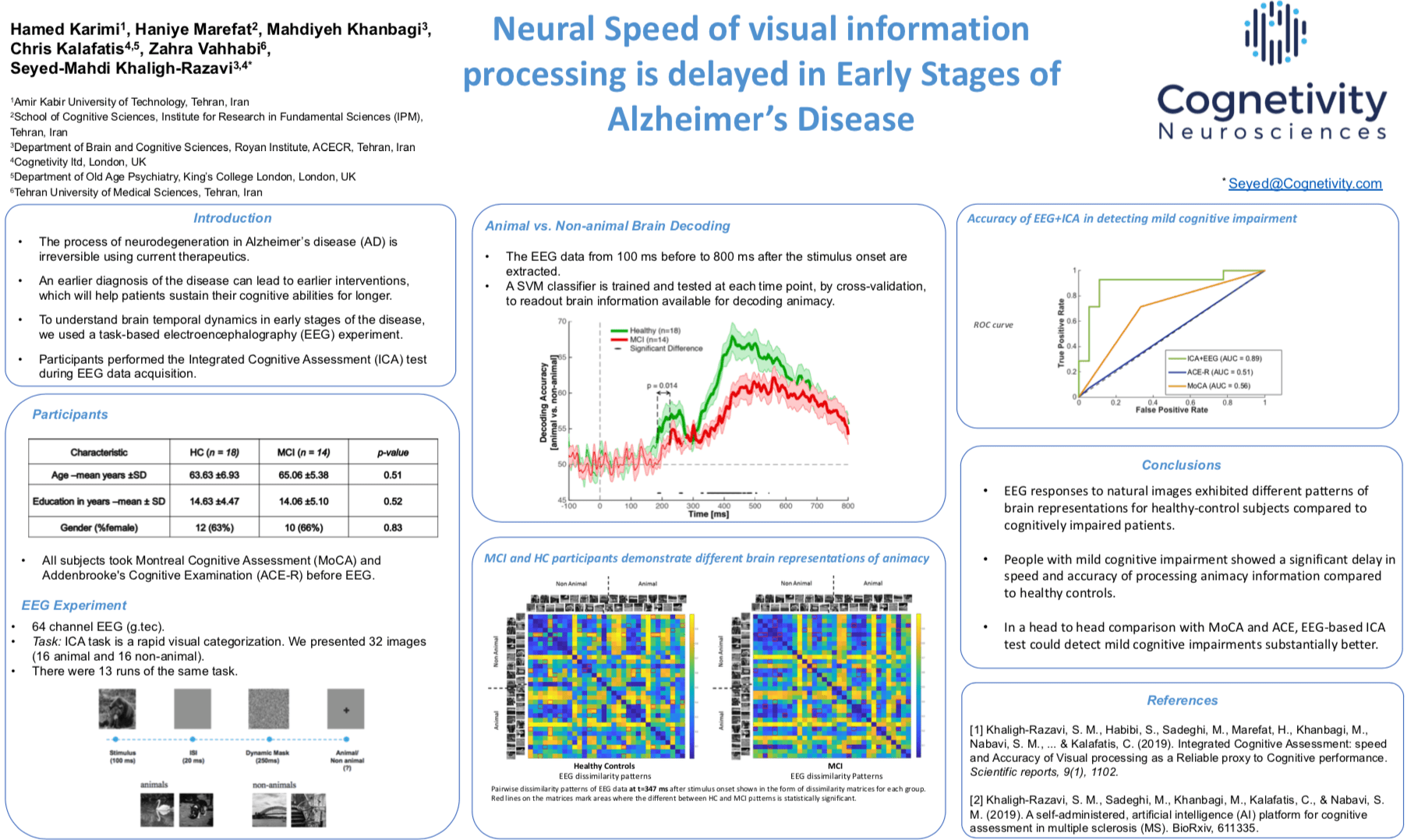
Introduction: Neurodegenerative disorders, such as Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), continue to represent a major economic, social and healthcare burden. These diseases remain underdiagnosed or are diagnosed too late for meaningful interventions. The development of screening tests capable of detecting AD during early, preferably asymptomatic, stages has been a highly unmet need. Since such tests will be used for screening large populations of people, they should be non-invasive, inexpensive, and ideally independent of language, education, culture and practice.
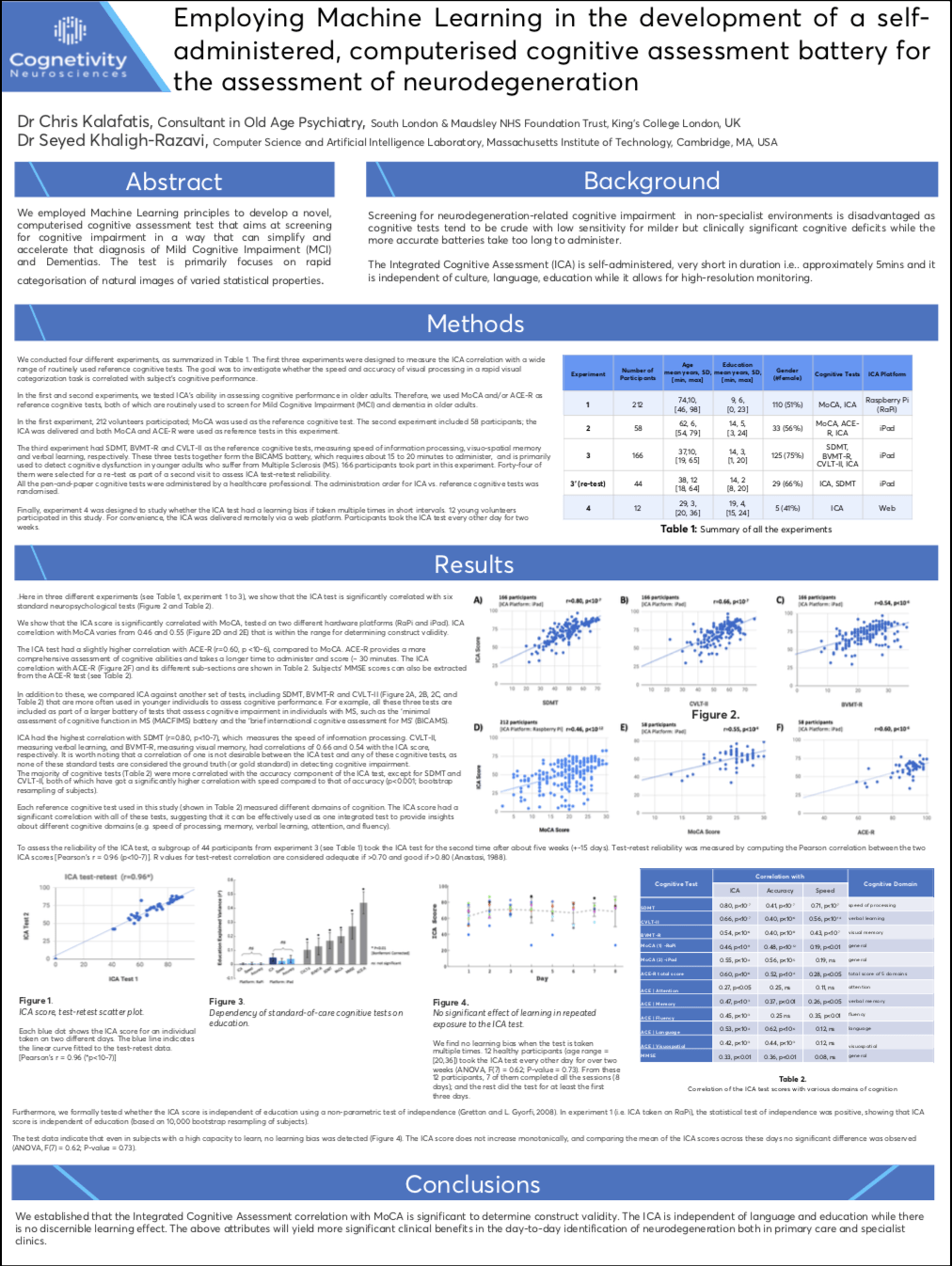
Materials and Methods: Taking advantage of new artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning techniques, we have developed a 5-minute integrated cognitive assessment tool (ICA) that meets the above-mentioned criteria, and has the flexibility to learn from new data to improve its predictive power. ICA is computerised, can be conducted without expert supervision, and is designed based on a rapid visual categorisation task, tracking participants’ response-patterns to natural stimuli to detect small changes in their cognitive performance.
Results: On a population of 268 participants (183 healthy, 85 cognitively impaired), ICA achieved an accuracy of 93%* in detecting cognitive impairment. Within those with cognitive impairment, ICA could discriminate mild cognitive impairment (MCI) from mild AD with 91%* accuracy. Furthermore in a task-based fMRI investigation, we find that the ICA task engages brain areas, such as transentorhinal, fusiform gyrus, inferior and middle temporal, that are anatomically identified among the earliest areas affected by tau-pathology in presymptomatic stages of AD, as shown by Braak and colleagues, 2006.
Conclusion: ICA engages brain areas affected in early stages of AD, and shows high sensitivity in detecting cognitive impairment. As such the test can be used as an aid for early diagnosis of AD, ideally even in presymptomatic stages, and is appropriate for large-scale screening of cognitive impairment, and micro-monitoring of cognitive performance.
*reported accuracies are area under the ROC curve .
 Loading...
Loading...